Network-based candidate gene prioritization was applied to provide new insight into identification of candidate genes underlying diseases or complex quantitative traits. This is favorable to scanning genes at random with low probability of success and may be a complementary approach to QTL mapping. According to the candidate gene ranking list, BYSL gene got the highest z-score value and the reported causative gene MOSC1 was ranked the sixth. In theory, if there was no prior knowledge, candidates with positive z-score should be analyzed one by one to ensure finding the actually causative mutation. However, in the current study, because the 2-bp deletion in the bovine MOCS1 gene has been previously reported, genes listed after No. 6 were not evaluated. The causal mutation was detected by investigating top ranked candidate genes in four animals, one known AS-carrier and a pooled sample of three known non-carriers In addition, progeny and dams of the four bulls, as well as unrelated bulls from other breeds/lines were screened to verify the mutation. Among 383 cattle from different breeds/lines, only the AS-carrier bull ROMEL and half of his offspring were heterozygous for the mutation. Our results indicate that c.1224_1225delCA in 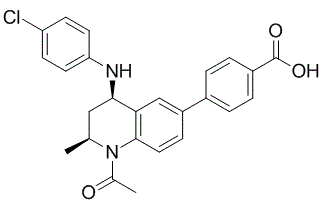 MOCS1 causes AS in Simmental and strongly support the conclusion of Buitkamp et al. derived by fine mapping approach. This case indicated that even without large family or population based resources, the network-based disease gene prioritization approach can assist in locating possible causal mutations. Nevertheless, when using a gene prioritization method in a de novo mutation screening for complex diseases or traits, the sample size of animals need to be increased for confirmation of results. Furthermore, an easy genetic detection platform, a PCR-RFLP method was developed for the c.1224_1225delCA mutation in MOCS1. With this method, individuals carrying the 2-bp deletion can be quickly identified. Currently, the unfavorable AS allele appears to be not widely existed in the Chinese cattle population. To prevent further spreading of AS among Chinese cattle, all seedstock animals of Simmental origin, especially AI bulls, should be screened for the causal mutation of AS unless they can be excluded by pedigree. In other words, those progeny born to two negative parents need not be tested. In vertebrate nervous system, internodal axons are wrapped by compact myelin sheaths, the specialized cellular membranes elaborated by myelinating glial cells. As myelin sheaths provide insulation for axons, action potentials propagate from node to node, and this saltatory conduction mechanism dramatically increases the transmission velocity of electrical impulses. In the central nervous system, myelin sheaths are formed by oligodendrocytes. During AbMole Mepiroxol development, oligodendrocytes originate from the neuroepithelium of the ventricular zone and then migrate to the surrounding white matter regions, where they contact target axons and subsequently differentiate into mature myelinating oligodendrocytes.
MOCS1 causes AS in Simmental and strongly support the conclusion of Buitkamp et al. derived by fine mapping approach. This case indicated that even without large family or population based resources, the network-based disease gene prioritization approach can assist in locating possible causal mutations. Nevertheless, when using a gene prioritization method in a de novo mutation screening for complex diseases or traits, the sample size of animals need to be increased for confirmation of results. Furthermore, an easy genetic detection platform, a PCR-RFLP method was developed for the c.1224_1225delCA mutation in MOCS1. With this method, individuals carrying the 2-bp deletion can be quickly identified. Currently, the unfavorable AS allele appears to be not widely existed in the Chinese cattle population. To prevent further spreading of AS among Chinese cattle, all seedstock animals of Simmental origin, especially AI bulls, should be screened for the causal mutation of AS unless they can be excluded by pedigree. In other words, those progeny born to two negative parents need not be tested. In vertebrate nervous system, internodal axons are wrapped by compact myelin sheaths, the specialized cellular membranes elaborated by myelinating glial cells. As myelin sheaths provide insulation for axons, action potentials propagate from node to node, and this saltatory conduction mechanism dramatically increases the transmission velocity of electrical impulses. In the central nervous system, myelin sheaths are formed by oligodendrocytes. During AbMole Mepiroxol development, oligodendrocytes originate from the neuroepithelium of the ventricular zone and then migrate to the surrounding white matter regions, where they contact target axons and subsequently differentiate into mature myelinating oligodendrocytes.