It is noteworthy that ALA-PDT treatment resulted in reduced MDR protein levels in HNC-derived CSCs after chemotreatment. The detailed mechanisms of the regulatory network between ALAPDT treatment on drug-resistant genes requires further investigation. In conclusion, the present study demonstrated the inhibitory effects of ALA-PDT on stem-like properties and chemoresistance in HNC. Notably, here is great need to unravel the underlying mechanisms of the ALA-PDT-mediated pathway in HNC-CSCs and to further evaluate the therapeutic possibilities of ALA-PDT treatment clinically. During spaceflight and simulated microgravity a human being is submitted to various environmental factors supposed or proven to induce morphological and functional disturbances on most of the physiological system of which we do not know exactly the degree of reversibility especially for the cardiovascular system. The impact of real or simulated microgravity on the main physiological systems is already well documented, while those of the confinement are not because in spaceflight it is difficult to distinguish between the role of these 2 factors and in bedrest there is no real confinement. Several studies of various duration were performed on healthy subjects to identify the impact of confinement and more precisely the role of the mental stress on the human being: ISEMSI 28days : �C EXEMSI 60days �C SFINCSS 110 d�C240 days HUBES – MARS 105days. Heart rate decreased during confinement, and oxydative stress increased. Renin, aldosteron, angiotensin, and arginin vasopressin increased. Creatinin increased in relation with reduced water intake and reduced physical activity. Cell and humoral immunity were decreased. Body weight and water loss and increased sodium were also reported. Lastly a reduction in rapid memory acuity was mentioned. The hypothesis of the MARS 500 experiment was that subjects in confinement may present vascular morphological and or functional changes in relation with the mental stress generated by the life in isolated condition or the environmental factors associated with the confined area. The objective was to investigate during and after the confinement period peripheral and central arteries and veins, as already done in other extreme environment like microgravity, bedrest, immersion during and after 520 day in confinement. A dedicated method based on echographic volume capture was used for the study to make the untrained and isolated subjects capable to capture images of the vessels without any assistance from outside. Before entering the module the subjects were trained 1 hour to perform on themselves a volumic capture of the organ/vessels they were supposed to investigate alone during the confinement period. The echographic investigation were always performed in seated position, because only this position allow self investigation by each volunteer. 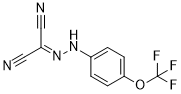 The subjects were taught to locate the echographic probe on top of the organ and make a TILT 10-Gingerol movement with the probe body, the probe head remaining at the same place on the skin. All the echographic views collected during the TILT were store as a video file on a hard disc, and sent later on to the Coptisine-chloride control center. Such maneuver does not require any practice in echography as the subject is not asked to perform a perfect long or short axis view of the vessel but only to scan the volume inside which the vessel is, by tilting the probe over 90 degree. Thus the subject have just to be minimally trained and keep capable to locate the probe on top of the acoustic window of the organ. In order to help the subject in locating the acoustic windows of each organ we identified the areas on the body with a high probability to find them.
The subjects were taught to locate the echographic probe on top of the organ and make a TILT 10-Gingerol movement with the probe body, the probe head remaining at the same place on the skin. All the echographic views collected during the TILT were store as a video file on a hard disc, and sent later on to the Coptisine-chloride control center. Such maneuver does not require any practice in echography as the subject is not asked to perform a perfect long or short axis view of the vessel but only to scan the volume inside which the vessel is, by tilting the probe over 90 degree. Thus the subject have just to be minimally trained and keep capable to locate the probe on top of the acoustic window of the organ. In order to help the subject in locating the acoustic windows of each organ we identified the areas on the body with a high probability to find them.