Moreover, 3,5-diaryl-2-aminopyridines resembling Erlotinib EGFR/HER2 inhibitor K02288 were recently discovered as anti-malarials, although we observed no effect of the lead compound on BMP or TGF-b signaling. K02288 exhibits remarkable potency for a low molecular weight screening hit, both in enzymatic assaysand in C2C12 cells. In comparison, the one previous screening hit dorsomorphin displayed IC50s of 50 nM in enzymatic 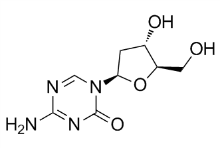 assaysand,0.5 mM in C2C12 cells. These activities were improved significantly following further chemistry to yield the lead derivative LDN-193189. Similar INCB18424 optimization of the cellular and in vivo activity of K02288 would be beneficial to fully exploit its significant selectivity and could be achieved by replacement of the potentially vulnerable phenol moiety. In the crystal structure of the ALK2-K02288 complex this group bound to the exposed solvent channel where substitutions are likely to be well tolerated. The discovery of diverse BMP inhibitor scaffolds establishes a repertoire of pharmacological tool compounds for cross-validation in investigations of cellular signaling. Moreover, the application of multiple orthogonal chemotypes may help to discern whether a particular toxicological liability is a class-wide pharmacological phenomenon due to ALK2 inhibition or the result of a chemotype specific off-target effect. The novel inhibitor K02288 provides an exciting new starting point for further chemistry with potential therapeutic applications in stem cell engineering, as well as in disease models of anemia, musculoskeletal dysplasia and cancer. Because many of the hits are rather hydrophobic/amphiphilic, they have the propensity to adsorb at the membrane or solution interface and thereby alter lipid bilayer properties, and thus be promiscuous modifiers of membrane protein function. As a complement to the liposome assay, we therefore employed a gramicidin channel assay to detect compounds with membraneperturbing properties. The assay uses the ion-conducting gramicidin channels that form by trans-membrane dimerization of two monomers from opposing leaflets of the bilayer. The gramicidin monomer?dimer equilibrium is sensitive to the membrane environment, making the gramicidins suitable to assay for membrane-perturbing effects. The bilayer-spanning gramicidin channels allow for the entry of monovalent heavy-ion quenchers, and the consequent quenching of fluorophore-loaded large unilamellar vesicles. The rate of fluorescence quenching is proportional to the number of conducting gramicidin channels, which will vary based on the membrane-perturbing effects of the added compounds. We measured the time course of fluorescence quenching in the presence of compound using the 8aminonaphthalene-1,3,6-trisulfonate /Tl+ fluorescence indicator/quencher pair. While more than 50% of the compounds produced a statistically significant increase in the fluorescence quench rate, one compound, 12G5, had a pronounced effectand was eliminated. Together, the liposome and gramicidin channel assay counter-screens eliminated six compoundsfrom further studies. Next, we used a hemolysis assay to further evaluate membranedisrupting potential or other cytotoxic properties against mammalian cells. One compoundcaused hemolysis and was excluded. The structures of the remaining 12 compounds were then inspected for potentially reactive groups, likely modifications in the human body that might generate reactive groups, and other features that might make the compounds non-selective as a starting point to construct chemical probes. The coumarin scaffold in compound 1G4 is associated with diverse pharmacologic actions, which might complicate its use for target identification.
assaysand,0.5 mM in C2C12 cells. These activities were improved significantly following further chemistry to yield the lead derivative LDN-193189. Similar INCB18424 optimization of the cellular and in vivo activity of K02288 would be beneficial to fully exploit its significant selectivity and could be achieved by replacement of the potentially vulnerable phenol moiety. In the crystal structure of the ALK2-K02288 complex this group bound to the exposed solvent channel where substitutions are likely to be well tolerated. The discovery of diverse BMP inhibitor scaffolds establishes a repertoire of pharmacological tool compounds for cross-validation in investigations of cellular signaling. Moreover, the application of multiple orthogonal chemotypes may help to discern whether a particular toxicological liability is a class-wide pharmacological phenomenon due to ALK2 inhibition or the result of a chemotype specific off-target effect. The novel inhibitor K02288 provides an exciting new starting point for further chemistry with potential therapeutic applications in stem cell engineering, as well as in disease models of anemia, musculoskeletal dysplasia and cancer. Because many of the hits are rather hydrophobic/amphiphilic, they have the propensity to adsorb at the membrane or solution interface and thereby alter lipid bilayer properties, and thus be promiscuous modifiers of membrane protein function. As a complement to the liposome assay, we therefore employed a gramicidin channel assay to detect compounds with membraneperturbing properties. The assay uses the ion-conducting gramicidin channels that form by trans-membrane dimerization of two monomers from opposing leaflets of the bilayer. The gramicidin monomer?dimer equilibrium is sensitive to the membrane environment, making the gramicidins suitable to assay for membrane-perturbing effects. The bilayer-spanning gramicidin channels allow for the entry of monovalent heavy-ion quenchers, and the consequent quenching of fluorophore-loaded large unilamellar vesicles. The rate of fluorescence quenching is proportional to the number of conducting gramicidin channels, which will vary based on the membrane-perturbing effects of the added compounds. We measured the time course of fluorescence quenching in the presence of compound using the 8aminonaphthalene-1,3,6-trisulfonate /Tl+ fluorescence indicator/quencher pair. While more than 50% of the compounds produced a statistically significant increase in the fluorescence quench rate, one compound, 12G5, had a pronounced effectand was eliminated. Together, the liposome and gramicidin channel assay counter-screens eliminated six compoundsfrom further studies. Next, we used a hemolysis assay to further evaluate membranedisrupting potential or other cytotoxic properties against mammalian cells. One compoundcaused hemolysis and was excluded. The structures of the remaining 12 compounds were then inspected for potentially reactive groups, likely modifications in the human body that might generate reactive groups, and other features that might make the compounds non-selective as a starting point to construct chemical probes. The coumarin scaffold in compound 1G4 is associated with diverse pharmacologic actions, which might complicate its use for target identification.